Source: Image Credit There are some basic requirements that a cryptographic protocol must satisfy in order to be considered secure. To this end, SSL and TLS protocols both present a combination of these properties:
The data connection is private as it is kept encrypted The protocol makes it possible to authenticate the identity of the communication peer using public key cryptographic mechanisms Every transmitted message ensures the reliability of the connection by including a message integrity check
Both the encryption protocols, SSL and TLS, strive to accomplish the same goal – increasing network communication security between the communicating peers. There are various security protocols that work in conjunction with SMTP to add additional security to your sensitive emails, so your mail is not transmitted in plain text which makes it vulnerable to being read by anyone who can intercept it. Some of these security protocols include SSL/TLS, Digital Certificates, Sender Policy Framework (SPF), Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM), Domain-Based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC), Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME) and Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)/OpenPGP. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and its successor, TLS (Transport Layer Security) help in email security and safeguard email privacy during their transition.
What is SSL/TLS?
Both SSL and TLS are cryptographic protocols that make use of encryption to secure communication over various computer networks. TLS is the upgraded version of SSL 3.0 and is now the de facto standard (though it is still common to refer to both the standards as SSL). SSL/TLS has found applications in a variety of scenarios, including securing data transmission using:
FTPS HTTPS SMTP, VoIP, etc.
Source: Image Credit There are some basic requirements that a cryptographic protocol must satisfy in order to be considered secure. To this end, SSL and TLS protocols both present a combination of these properties:
The data connection is private as it is kept encrypted The protocol makes it possible to authenticate the identity of the communication peer using public key cryptographic mechanisms Every transmitted message ensures the reliability of the connection by including a message integrity check
Both the encryption protocols, SSL and TLS, strive to accomplish the same goal – increasing network communication security between the communicating peers.
How does SSL/TLS encryption work?
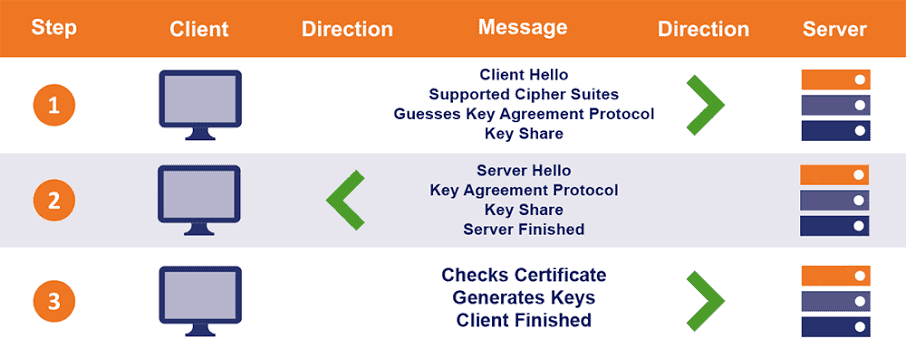
A TLS communication session begins with what is known as a TLS handshake. The handshake typically uses asymmetric encryption, which means that both the ends use a different key at their end using a mechanism known as public key cryptography. Public key cryptography makes use of two keys: a public key made available to the public by the server; and a private key, which is used only by the server and kept secret from everyone else. Data encrypted with the private key can only be decrypted by using the public key, the reverse also holds true. The server and the client use private and public keys to generate random data that they exchange during the TLS handshake. This random data is then used to create new security keys, called session keys, for encryption. Every new encrypted communication session makes use of different security keys. You need to purchase Symantec SSL certificate to install on the server. It is the data file that contains your server’s public key along with its ownership/domain information. You cannot make use of SSL/TLS encryption to protect your traffic unless you have installed an SSL certificate on your server. Here is an outline of how the TLS handshake works:
Source: Image Credit
How do you use SSL/TLS to protect your email?
The language (protocol) and mechanism used by one email server to send email messages to another email server is known as SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol). Almost all email servers have the option of making use of TLS to secure and protect the privacy of their emails by encrypting the message transmission over the internet. Using TLS with SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol ) guarantees that the email content is guarded against “man in the middle” attacks while it is transmitted between the email servers. It is easy to set it up once you have installed an SSL certificate on the email server.
Source: Image Credit When your users engage regular POP or IMAP to access their emails, sensitive information such as their username and password are transmitted in clear text over the network. This makes it easy for anyone to hijack the communication and read their emails, even send out spam emails from their account. The users must be directed to encrypt their connections to the email servers using SSL/TLS in their mail clients running on their PC or a corresponding app on their tablet or smartphone. The most important thing to know here is what ports are being used for receiving and sending emails. These options are available in the account settings section of the email program. There will also be a general option for enabling SSL/TLS encryption for email transmission. As soon as it is turned on, the email program will usually set the correct ports automatically. In case, users need to manually configure the SSL/TLS ports for secure email transmission, here are the common settings:
Incoming mail server (IMAP) – port 993 Incoming mail server (POP3) – port 995 Outgoing mail server (SMTP) – port 465
Hope this answers your questions related to using SSL/TLS to secure and protect the privacy of your emails.
Resources